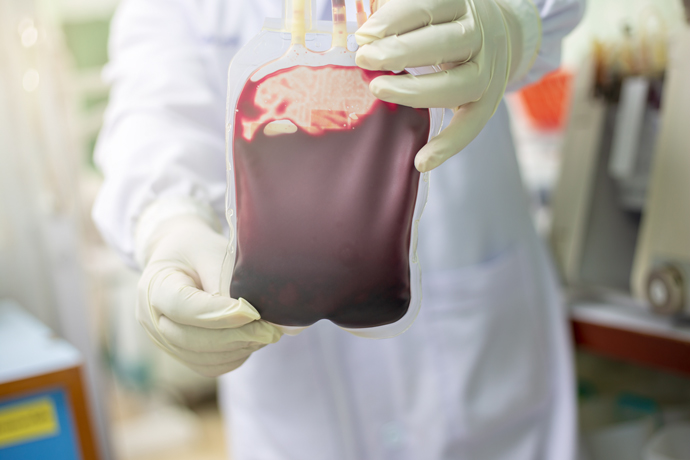
Umbilical cord blood is the blood found in a newborn baby’s umbilical cord. Expecting parents have the once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to collect and preserve the umbilical cord blood stem cells for many years. This collection and preservation practice is called cord blood banking. After the birth of the baby, once the umbilical cord is clamped and cut – the remaining cord blood is collected using a specialised collection kit and sent to a private cord blood bank laboratory for testing, processing and storage in liquid nitrogen tanks for years, until needed for transplant.
The umbilical cord blood is an abundant source of master or ‘naive’ cell that can transform into specialised cells depending on where it is needed in the body. These properties make them extremely valuable in medicine.
Umbilical cord blood stem cells are currently being used to treat more than 85 medical conditions and is currently being used in clinical trials for treating autism, heart damage, brain injury, hearing loss, blindness and even Alzheimer’s disease.
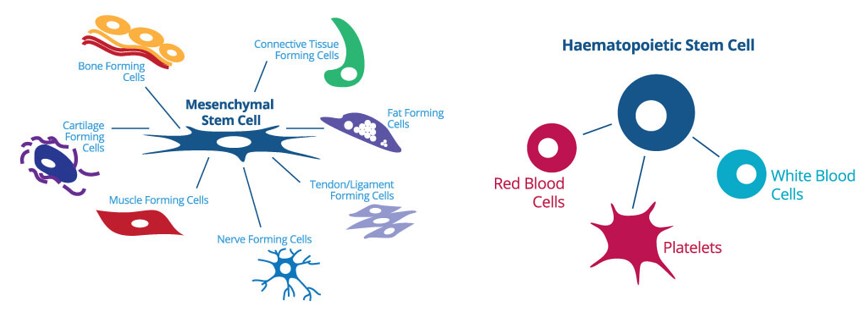
Major stem cell types found in the cord blood:
- Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) – These cells have the ability to transform into various blood cells, including white blood cells.
- Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) – These cells have the ability to transform into a huge range of tissue types, including nerve tissue, muscle tissue, and cartilage. With these features they are considered extremely important for regenerative therapies.
- Very small embryonic-like stem cells (VSELs) – These cells can transform into a wider array of tissue types than most other stem cell types.
 Many parents, including some celebrities, decide to store their baby’s umbilical cord blood to help protect their baby and their family’s health in the future. By saving the umbilical cord blood stem cells with a private cord blood bank, you have the exclusive ownership of the stem cells stored. And you can be assured that this valuable material will be available if ever your child or any of your family member requires a stem cell transplant in the future.
Many parents, including some celebrities, decide to store their baby’s umbilical cord blood to help protect their baby and their family’s health in the future. By saving the umbilical cord blood stem cells with a private cord blood bank, you have the exclusive ownership of the stem cells stored. And you can be assured that this valuable material will be available if ever your child or any of your family member requires a stem cell transplant in the future.
Watch: Why Parents Save the Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells?
At Cells4Life, we offer three different cord blood storage options for parents-to-be:
1. Volume-reduced cord blood storage – focuses on extracting the maximum amount of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from the umbilical cord blood by using the AXP technology.
2. Whole cord blood storage – captures MSCs, HSCs, VSELs, and other stem cell types present within the umbilical cord blood including other hormones and growth factors.
3. CellsPlus – using TotiCyte, a ground-breaking cord blood separation technology patented and exclusive to Cells4Life that delivers 3x more stem cells at the point of treatment than any other method.
4. Cord Tissue – this is an add-on services that stores a piece of the umbilical cord which is also rich in mesenchymal stem cells. It also contains valuable cells that are not present in the cord blood such as vascular endothelial stem cells, perivascular stem cells, and unrestricted somatic stem cells (USSCs) which also expected to have great therapeutic benefit in the future.
We also provide expecting parents the unique option of:
5. Placenta Banking – captures the placental cells from chorionic villi which are being investigated to treat heart disease, ostearthritis, type 2 diabetes and more.
6. Amnion Banking – stores the amnion (inner layer of the placenta) which have been used to treat wounds and burns since the 20th century.
Watch: Cells4Life Services
Cord blood collection is a short, simple and safe procedure for both the mum and baby since it doesn’t interfere with the labor or birth and only takes place after the umbilical cord is detached from the baby. This is usually performed by the doctor or midwife attending the birth.
Watch: How Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cell Collection Works
Stem Cell Transplant Using Cord Blood Stem Cells
The purpose of using stem cells for transplant is to replace unhealthy cells, which is one of the most common medical procedures nowadays. These stem cells are derived from two common sources — umbilical cord blood and the bone marrow.
A bone marrow transplant procedure requires a transplant from a donor to the recipient in order to cultivate new stem cells. Bone marrow grafts need to be a perfect match. However, a cord blood transplant can be carried out even if the match is partial. Cord blood contains nearly 10 times more stem cells than bone marrow. And stem cells found in cord blood have greater regenerative properties since they are younger than those found in bone marrow.
1) Reduce Graft vs Host Disease (GvHD)
Graft rejection occurs when the recipient’s body rejects the newly transplanted stem cells. Using cord blood is preferred for transplant as the stem cells found in cord blood are less likely to attack the patient’s tissues even if the donor is not related.
2) HLA Match
If you share the same Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA) with someone, your tissues are immunologically compatible. Since HLA protein is inherited, a family donor is likely to match exactly. Since 70% of recipient’s do not have a suitable family donor, using umbilical cord blood stem cells for transplant is a better choice as they adapt more easily.
Read More: Why HLA matching is important before a cord blood transplant?
3) Easier Cord Blood Availability
Stem cell transplants are needed by more than 30,000 patients annually and a suitable bone marrow donor is not so easily available. About 70% of patients cannot find an exact match which proves fatal for many cancer patients. Cord blood banking has proved to be savior as patients are likely to get a suitable donor from public banks and for those who stored their own umbilical cord blood stem cells.
4) Painless Procedure
From a donor’s perspective, bone marrow donation requires an invasive procedure with general anesthesia. This procedure is not needed for cord blood donors as the blood is collected right after the birth when the baby’s umbilical cord is clamped and cut.
Want to learn more about the benefits of saving the umbilical cord blood stem cells? Speak to one of our cord blood banking specialists now at +971 4 3116613 or send us an inquiry
{{cta(‘7d7cc8da-ed20-48a8-8ef3-e2429767260f’)}}